The purpose
A Chrome extension modifies specific web pages.
This modification is client-side only; it does not edit server-side files and is only effective on the PC where the extension is installed.
Environment
Chrome:112.0.5615.138
Regarding the extension’s manifest
extension’s manifest:V3
Many Chrome extensions explained on pages appearing in current searches are manifest Version 2 (V2).
V2 is scheduled for eventual discontinuation, so it’s advisable to use V3 whenever possible. Also, some pages mention V2’s discontinuation in 2023/1 or 2023/6; however, this information is incorrect or outdated.
Currently (as of May 2023), no specific discontinuation date has been set.
For more details, please refer to the following page:
Creating and adapting extensions
Extension Overview
Addition
To modify a specific page using a Chrome extension, the extension is generally built to function as follows
- Arbitrary JavaScript is automatically executed when the page is displayed.
- The executed JavaScript modifies the displayed page.
Creating extensions
Folder structure
Create an arbitrary folder (e.g., “extension”) and create a manifest.json file and an arbitrary JavaScript file (e.g., “sample.js”) within it.
\---extension
manifest.json
sample.jsCreate manifest.json
For extensions that allow modification of arbitrary pages, the manifest.json file should at least include the following.
The manifest.json file declares the nature of the extension being created.
{
"name": "Sample",
"version": "1",
"manifest_version": 3,
"content_scripts": [
{
"matches": [ "https://blog.en.marunokan.com/*" ],
"js": ["sample.js"]
}
]
}Here are the meanings of each item.
| Item name | |
| name | Extension Name (Optional) |
| version | Extension Version (Optional) |
| manifest_version | Manifest version: fixed at 3. |
| content_scripts | As explained under Extension Startup Conditions |
The meaning of content_scripts is as follows
| Item name | |
| matches | The page to execute. Adding a * at the end allows execution in subfolders as well ( * can also be used in the middle). |
| js | The JavaScript file executed on the page specified by matches |
The example above declares an extension using manifest version 3, named “Sample”, version 1, that executes “sample.js” (including subfolders) on the page “https://blog.en.marunokan.com/”.
JavaScriptファイルの作成
create the JavaScript specified in the ‘js’ folder under ‘content_scripts’ (in this example, sample.js).
document.getElementById("header-in").innerHTML += "<div><a href='./' target='_blank'>新しい Window<a/></div>";In this example, I created JavaScript code that inserts a link that opens a new window, as shown above.
Registering an extension
register the extension I created with Chrome.
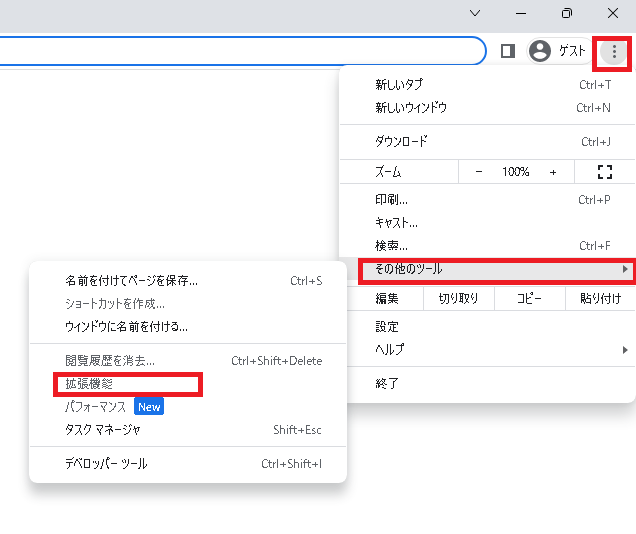
Open Chrome and select the three vertical dots next to your username, then go to “More tools” -> “Extensions”.
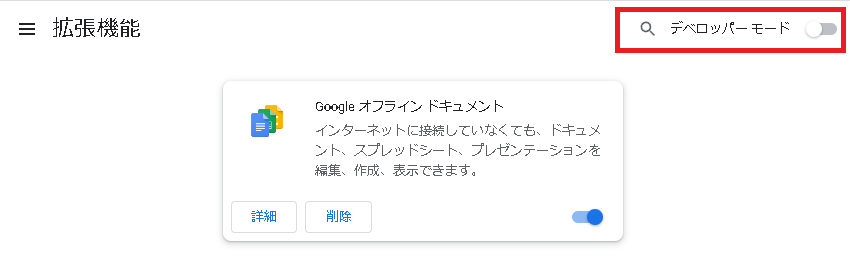
表示された画面右上の”デベロッパーモード”をオンにします。
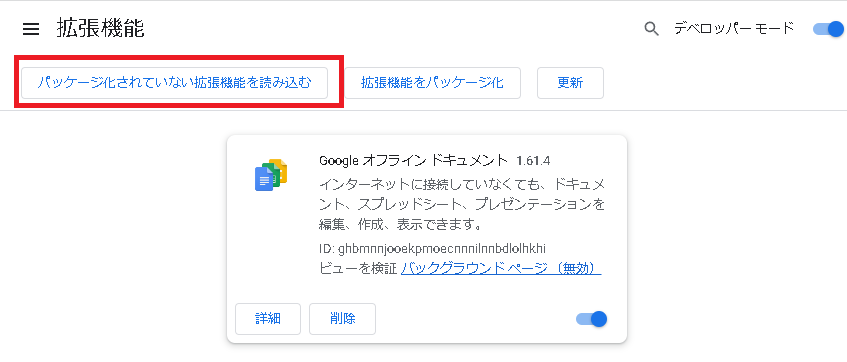
Turning on “Developer mode” will add a button to the top. Click “Load unpacked” button.
A file selector will open; with the folder containing your manifest.json file open, click “Select Folder”.

If you see the extension you created as shown above, you’ve succeeded.
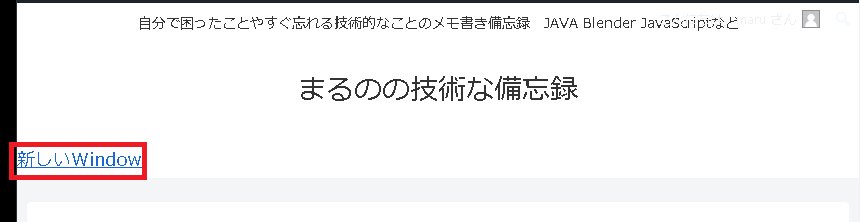
Result
A link has been added that opens https://blog.en.marunokan.com/ in a new window (tab) when clicked.


comment